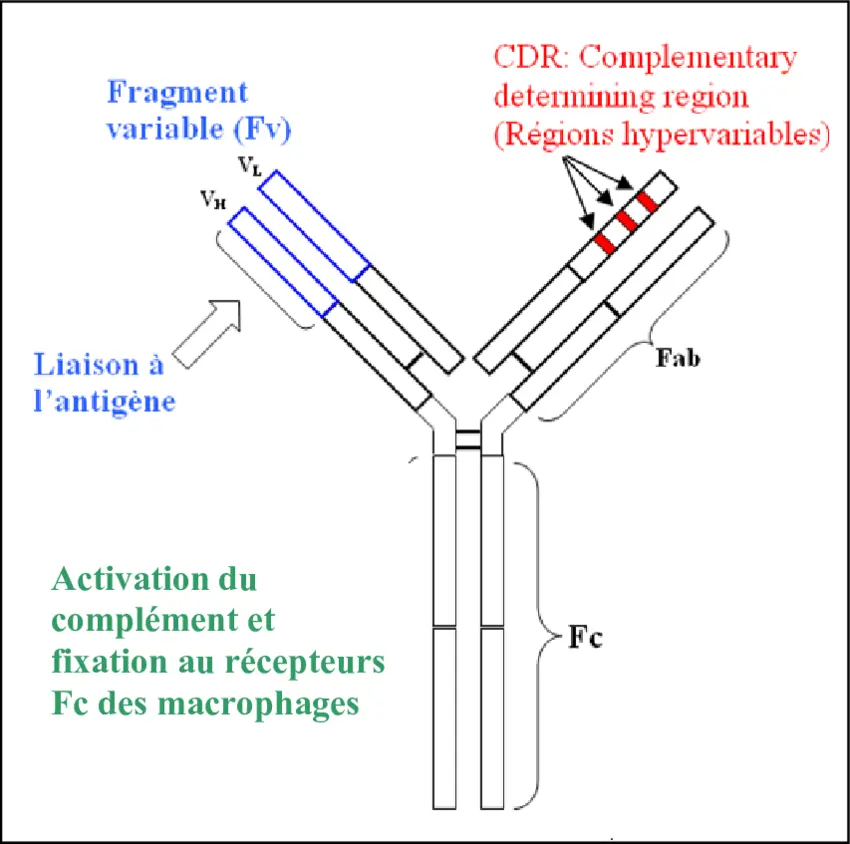
Specialized proteins called immunoglobulins (Igs), also referred to as antibodies, are made by B lymphocytes and are essential to the immune system. They aid the body's efficient self-defense by recognizing and eliminating foreign invaders such as bacteria, viruses, and poisons. Immunoglobulins are divided into five main classes, each with unique functions and structures designed to provide different forms of bodily protection.
For researchers, students, and anybody else interested in immunology or the biomedical sciences, it is essential to comprehend these courses.
Isotypes :
🧪 IgG — The Most Abundant and Versatile Antibody
Structure: Monomer
Functions:
- Provides long-lasting immunity after infection or vaccination
- Neutralizes viruses and bacterial toxins
- Activates complement system and promotes phagocytosis
- Crosses the placenta to protect the fetus
🌊 IgA — The Guardian of Mucosal Surfaces
Structure: Mostly dimeric
Functions:
- Prevents pathogens from attaching to mucous membranes
- Protects respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts
- Supports newborn immunity through breast milk
- Maintains healthy gut microbiota
⚡ IgM — The First Responder
Structure: Pentamer
Functions:
- First antibody produced during new infections
- Potent activator of the complement system
- Clumps pathogens for easier elimination
🔥 IgE — Defender Against Parasites and Mediator of Allergies
Structure: Monomer
Functions:
- Protects against parasitic worms
- Triggers allergic reactions via histamine release
- Involved in asthma, hay fever, and hypersensitivity
IgD — The Mysterious Antibody
Structure: Monomer
Functions:
- Acts as a receptor on B cells
- May play roles in respiratory immune defense
- Function still under active research
🔍 Why Understanding Immunoglobulin Classes Matters
The diversity of immunoglobulin classes reflects the immune system’s adaptability. Each class specializes in different locations and types of immune responses, ensuring comprehensive protection. This knowledge is foundational for:
- Designing effective vaccines that stimulate the right antibody response
- Developing antibody-based therapies and diagnostic tools
- Understanding allergies, autoimmune diseases, and immunodeficiencies
🚀 Future Perspectives in Antibody Therapeutics
- Development of multi-specific and bispecific antibodies targeting multiple disease pathways simultaneously.
- Integration of gene therapy to deliver long-lasting antibody expression.
- Creation of synthetic antibodies designed by computational methods for precision targeting.
- Expansion of antibody therapy to novel targets, including intracellular proteins and complex diseases.
To sum up, immunoglobulins are essential players in our immune defense, each with its own special role. Knowing how they work helps us understand health, disease, and new treatments better.